In a new survey, Trusted Future found Americans are adopting a broad range of connected health technologies to improve their daily lives, and believe emerging technologies hold great promise for helping people improve health outcomes, live healthier lifestyles, improve preventative care, and gain access to remote care anytime, anywhere. But to enable these health gains – and help Americans live longer and healthier lives – consumers need to be able to trust that their technologies will be effective at protecting their most sensitive health data.
Over the last few years, major breakthroughs in connected health technologies have enabled Americans to improve their health in previously unimaginable ways. Smartphones, for example, have put many of these advances right in the palms of our hands, on our wrists, and increasingly in our future. Wearables, connected devices, and software apps are empowering users to take greater control of their own health with tools that help users live longer, healthier, more fulfilling lives. Together, these technologies are driving one of the biggest and most fundamental transformations in health care.
The survey found that many Americans are already making use of connected healthcare technologies in their daily lives:
65% use connected health technologies to answer simple medical questions such as through a web search or by asking a virtual assistant
49% use or have used health apps to set and reach fitness, mindfulness, weight loss, and other goals
45% store health related data on their mobile devices like information from their doctor, hospital, a medical ID, or health status
41% report using smartwatches or other wearables to improve sleep quality, fitness, or other aspects of their health
30% are using smart apps or devices that monitor activity to proactively detect health conditions (like heart problems) and alert the wearer so they can preventatively receive care
Respondents also expressed concerns, including:
About their private data being sold without their consent (82%)
Shared with others without permission (82%), or
Being lost or stolen and subsequently showing up in public (81%)
Given the increasingly pervasive role technology is playing in our daily lives, Trusted Future launched a comprehensive national survey of 2,414 Americans conducted by YouGov to better understand how consumers are using these technologies to improve health, the barriers they feel must be overcome, and the potential steps policymakers can take to further improve connected health outcomes.
Several high-level findings jump out: connected health technologies are already being widely adopted and impacting lives in positive and profound ways. And while harnessing these connected health innovations holds great promise for driving better care, and faster cures, whether and how quickly we achieve these gains is fundamentally dependent on a consumer’s ability to trust that technologies are effective, affordable, and designed with privacy and security safeguards built in.
FIVE KEY THEMES: HOW RESPONDENTS VIEW THEIR CONNECTED HEALTH FUTURE
Americans see important potential benefits from connected health technologies.
Americans recognize the impacts, big and small, that connected health technology promises to deliver. Respondents believe they can bring substantial benefits and predict that connected health technologies are likely to contribute in important ways, like to:
Help people take their medicine on time (53%)
Reduce paperwork and time spent filling out healthcare forms (51%)
Give people greater control over their own health (49%)
Prompt research that will lead to new ways to diagnose and treat medical conditions (46%)
More effectively treat chronic conditions, like diabetes and heart disease (47%)
Help provide more personalized care (45%)
Help improve early disease diagnosis and warnings (45%)
Broaden access to high quality care to more people (43%)
Help people stay fit (41%)
Americans value their unprecedented access to quality health information.
Americans today have unprecedented access to health information, whether it be answers to medical questions or insights from data collected by their wearable. When asked which features they find most attractive, (54% and 51%) expressed support for (1) smart apps or devices that can monitor activity to proactively detect heart and other health conditions and (2) for wearable health monitoring devices that help users improve sleep quality, fitness, or other aspects of their health. All of these technologies rely on sensors to generate health related data, which is then transformed into actionable insights enabling us to act upon it in meaningful and helpful ways. This and other health related data and information can be sensitive, must be protected, and must be stored – often directly on one’s personal smartphone. In fact, when asked how they use various technologies, 45% of respondents report that they currently or previously have stored health care data on their mobile devices like information from their doctor, hospital, a medical ID, health records, prescriptions, or a woman’s health status. This explains why 51% of respondents said they are more likely to trust technology when third parties are prevented from accessing the health information stored on their mobile device without their explicit permission, showing the importance of baking in privacy protections.
Americans believe connected health technology can ensure broader and more equitable access to high-quality healthcare.
A plurality of respondents believe these connected technologies will help broaden access to high-quality care to more people. That’s important because 64% thought it is important to make affordable high-quality care available for everybody, “because no one should be forced to put their life at risk simply because they live too far from a doctor.” To ensure broader and more equitable access to connected health technologies, respondents identified three important ways policymakers could act: 1) by ensuring ubiquitous access to broadband, 2) by connecting every rural health clinic with high-speed broadband, and 3) by extending the virtual health care rules adopted during the pandemic that expanded access to telemedicine, so they don’t expire.
The opportunities emerging from telehealth technologies are already evident when anyone with a smartphone, tablet, or laptop can connect to remote care. The survey, for example, found that telehealth technologies are being widely adopted, with more than half (52%) saying they have used technology to connect and communicate with their doctor remotely. 49% believe it will expand opportunities for patients to receive a diagnosis and treatment remotely. This builds on previous research that has found more than half of physicians reported using telehealth to treat patients, compared with 18 percent just two years earlier. Americans are optimistic that these connected health technologies will reduce barriers and lead to more equitable outcomes.
At the same time, 48% believe that connected health technology will also improve senior care. Falls are a leading cause of injury and death among Americans aged 65 and above and more than 25% of older adults will fall each year, according to the CDC, and Americans believe that connected health technologies have a role to play in keeping older adults safe. Smartwatches can now detect falls and call for help when needed, which 68% of respondents said was positive, including 81% of seniors over the age of 65. Americans also want our devices to be accessible to all users, including older adults and persons with disabilities, with 57% of respondents saying accessibility features built into technology, such as large fonts or text dictation, made a device more attractive.
Connected devices are also transforming how Americans monitor and manage their health.
Smartwatches and other wearable devices are increasingly being designed with sophisticated sensors capable of monitoring a user’s health and detecting disease indicators. According to a study published in JAMA Cardiology, an Apple Watch app developed by Cardiogram was able to detect atrial fibrillation with 97% accuracy.
53% of survey respondents said they found smart apps or devices to monitor for health conditions, like heart problems, that can alert the wearer so they seek preventive care, attractive
49% of respondents likewise said they found wireless health devices capable of connecting to the user’s phone to track health indicators, such as “smart” thermometers, scales, blood pressure cuffs or glucose monitors, attractive
Americans are using connected health technology to take ownership of their health.
Mobile health technologies are being broadly used to track general fitness and health. To help tackle the challenge of getting more people to eat well and exercise, innovators have created more than 340 consumer wearable devices, more than 325,000 separate smartphone health apps, and are adding 200 new health apps each day. These new apps and wearables are leading to a new generation of empowered patients who are increasingly taking ownership of their own health beyond the walls of a doctor’s office. For example, researchers at Stanford found that the closer people track their weight-loss efforts with things like smart watches, digital scales and diet-monitoring apps, the more weight they tend to lose.
The survey bore this out:
49% said they have used apps to help set fitness goals, to become more active, mindfulness or wellness app(s) to help meditate, brain/puzzle apps to sharpen their mind, or weight loss apps to help count calories or obtain health goals
51% find wearable health monitoring devices like a smart watch or fitness band, are attractive ways to improve sleep quality, fitness, or other aspects of their health
58% rated as positive the fact that there are now more than 300,000 health-related applications available for download to a mobile device (apps to help track and improve health in areas like diet, fitness, weight loss, heart health and brain games)
TRUST IS A CENTRAL ELEMENT IN HOW BROADLY BENEFITS ARE SHARED
For connected health benefits to reach consumers, users must be able to trust that the devices are effective, affordable and designed to safeguard their privacy and data security. When deciding to adopt a new connected health technology, respondents rated the effectiveness of a connected health technology as their most important criteria—41% said it was either first or second in importance when they consider using a connected health technology; 29% and 30% said the same with respect to security and privacy.
People are unlikely to adopt potentially beneficial health technologies if they don’t trust that it will work effectively, or if it could put their personal privacy at risk. Respondents say they are concerned about ensuring that their health data is kept secure and private. This is understandable, healthcare data is some of the most personal and intimate information anyone keeps. Respondents expressed concern:
About their private data being sold without their consent (82%)
Shared with others without permission (82%), or
Being lost or stolen and subsequently showing up in public (81%)
CONSUMERS IDENTIFY KEY WAYS TO FOSTER TRUST IN TECHNOLOGIES
The survey found that citizens are more likely to adopt potentially beneficial connected health technologies if they trust the technologies are effective, affordable, protect their privacy and data. When asked what could lead them to trust connected health technologies more, respondents delivered a consistent message regarding the importance of designing devices and services to protect user privacy and data.
CONSUMERS ARE MORE LIKELY TO TRUST CONNECTED TECHNOLOGIES WHEN:
EXPLICIT CONSENT
Companies are prevented from collecting and selling sensitive location and other sensitive 59% information without your explicit consent.

31%: Trust Technology Much More
28%: Trust Technology Somewhat More
ENCRYPTION
The messages between you and your doctors are protected with strong encryption that ensures that no one but you and your intended recipients are able to read your messages.

29%: Trust Technology Much More
30%: Trust Technology Somewhat More
SAFE KEY STORAGE
The personal health data you have stored is backed up in an encrypted way (‘lock box’) where only you have the key to unlock it.
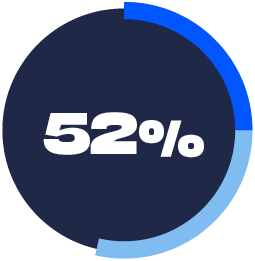
25%: Trust Technology Much More
27%: Trust Technology Somewhat More
NO THIRD PARTY ACCESS
WITHOUT PERMISSION
Third parties are prevented from accessing the health information stored on your mobile device without your explicit permission.
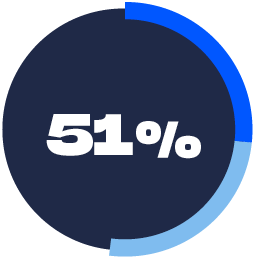
26%: Trust Technology Much More
25%: Trust Technology Somewhat More
APP VETTING ACCORDING TO
PROFESSIONAL STANDARDS
Apps are vetted by professionals to weed out scams and remove apps that put user privacy or data security at risk.

23%: Trust Technology Much More
27%: Trust Technology Somewhat More
PRIVACY BUILT IN
Comprehensive privacy protection is built into devices, apps, and services.
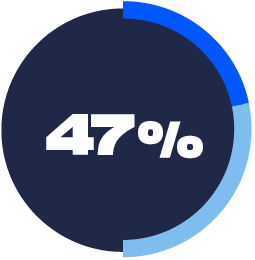
23%: Trust Technology Much More
24%: Trust Technology Somewhat More
BEST SECURITY AND PRIVACY PRACTICES
Devices and services use recognized best practices to keep user information secure and private.
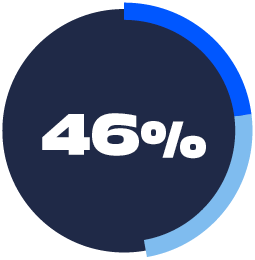
20%: Trust Technology Much More
26%: Trust Technology Somewhat More
PRIVACY LABELS
You have easy to use privacy labels that help you understand what data is being collected and shared by the apps you use.

20%: Trust Technology Much More
25%: Trust Technology Somewhat More
KEY STEPS POLICYMAKERS CAN TAKE TO FURTHER IMPROVE CONNECTED HEALTH OUTCOMES
Policymakers have an important role to play too. To improve trust in digitally connected health technologies, survey respondents identified key steps policymakers could take. Policymakers, they said, should:
Reject efforts that have the effect of weakening strong encryption, and encourage the efforts of companies to protect their customers by deploying strong encryption (52%)
Comprehensively evaluate the privacy, security, and safety impacts of any technology-related policy proposal or legislation, before it goes into effect (51%)
Write comprehensive privacy protections into law (46%)
Ensure underserved communities have access to reliable, relevant and trusted information (42%)
Extend virtual health care rules adopted during the pandemic that expanded access to telemedicine, so they don’t expire (40%)
Connect every rural health clinic with high-speed broadband (40%)
Enable everyone to take full advantage of health technologies by ensuring ubiquitous access to broadband (35%)
SUMMARY: A MORE TRUSTED FUTURE IS A HEALTHIER FUTURE
Connected health technologies are already being widely adopted and impacting Americans in positive and profound ways. And while harnessing these connected health innovations holds great promise for driving better care, and faster cures, whether and how quickly we achieve these gains is fundamentally dependent on a consumer’s ability to trust that technologies are effective, affordable, and designed with privacy and security safeguards built in. Respondents want policymakers to support strong encryption, comprehensive privacy protections, expand equitable access to high-quality healthcare, and continue access to telehealth technologies.
